What Molecule Does Fermentation Provide to Glycolysis
Amino acids provide the carbon skeleton for the synthesis of glucose. What is important to r ecognise is that ultimately all the food that is respired.

Yeast Energy Metabolism Yeasts Have Two Pathways For Atp Production Download Scientific Diagram
Glycolysis from Greek word glykys meaning sweet and lysis meaning dissolution or breakdown can be defined as the sequence of enzymatic reactions that in the cytosol also in the absence of oxygen leads to the conversion of one molecule of glucose a six carbon sugar to two molecules of pyruvate a three carbon compound with the concomitant production of two.

. The process is a reverse of glycolysis and takes place in two steps. Glucose is trapped by phosphorylation with the help of the enzyme hexokinase. RESPIRATION IN PLANTS 227 directly herbivores or indirectly carnivores.
Dillon in Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology Second Edition 2014 Diacetyl. Glycolysis is a cytoplasmic pathway which breaks down glucose into two three-carbon compounds and generates energy. The presence of lactate and an increase in temperature from 21 to.
The second step is the reverse of. Saprophytes like fungi are dependent on dead and decaying matter. When oxygen and hydrogen combine to form water at the end of the electron transport chain that is an example of an anabolic process where smaller molecules combine to make a larger molecule.
In the first step the carbon skeleton of an amino acid is converted into pyruvic acid or pyruvate within the mitochondria. 142 Glycolysis 143 Fermentation 144 Aerobic Respiration 145 The Respiratory Balance Sheet 146 Amphibolic Pathway 147 Respiratory Quotient 2021-22. In this process glucose is broken down into pyruvate.
Adenosine triphosphate ATP is used in this reaction and the product glucose-6-P inhibits hexokinase. Glycolysis takes place in 10 steps five of which are in the. The pyruvate molecule is then transported outside the mitochondria into the cytoplasm.
Diacetyl 23-butanedione and its reduced forms acetoin and 23-butanediol are produced by the metabolism of sugars via pyruvate. Diacetyl production however is low unless there is an additional source of pyruvate citrate or acetate. Glycolysis is an example of a catabolic cellular process.
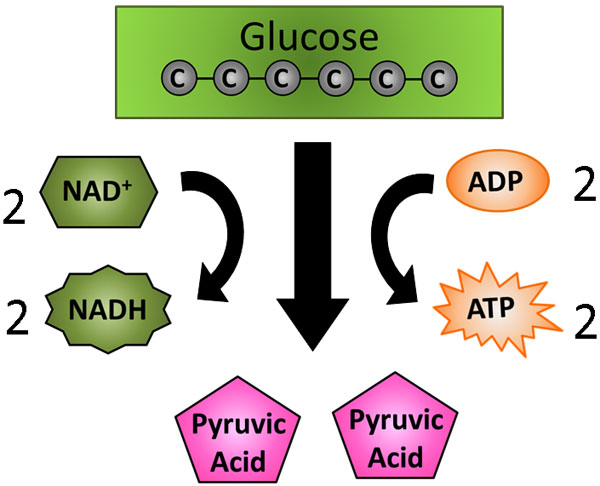
Cell Processes Fermentation Texas Gateway
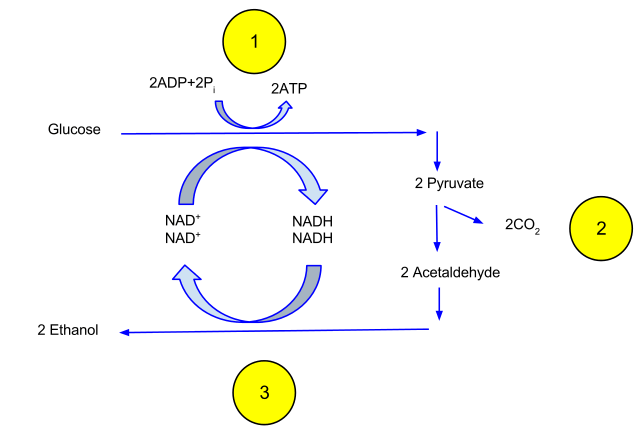
Fermentation Mitochondria And Regulation Biological Principles

Cellular Respiration Glycolysis And Fermentation Diagram Quizlet

Cellular Respiration Is Glycolysis The Beginning Part Of Fermentation Or Does Fermentation Follow Glycolysis Biology Stack Exchange

Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Cellular Metabolism And Fermentation
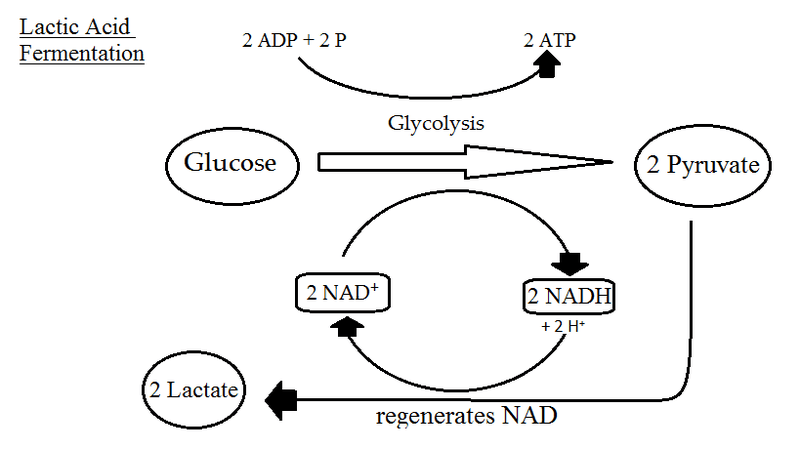
Fermentation Mitochondria And Regulation Biological Principles

Fermentation Anaerobic Glycolysis Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis And The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Mcat Content

Types Of Fermentation Biology For Majors I

Glycolysis And Fermentation Diagram Diagram Quizlet

Chp 4 6 Fermentation Study Guide Set Flashcards Quizlet
Glycolysis And Fermentation Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Process Cycle Life Used Molecules Energy
Cellular Metabolism And Fermentation
Glycolysis And Fermentation Updated Youtube
Cellular Metabolism And Fermentation
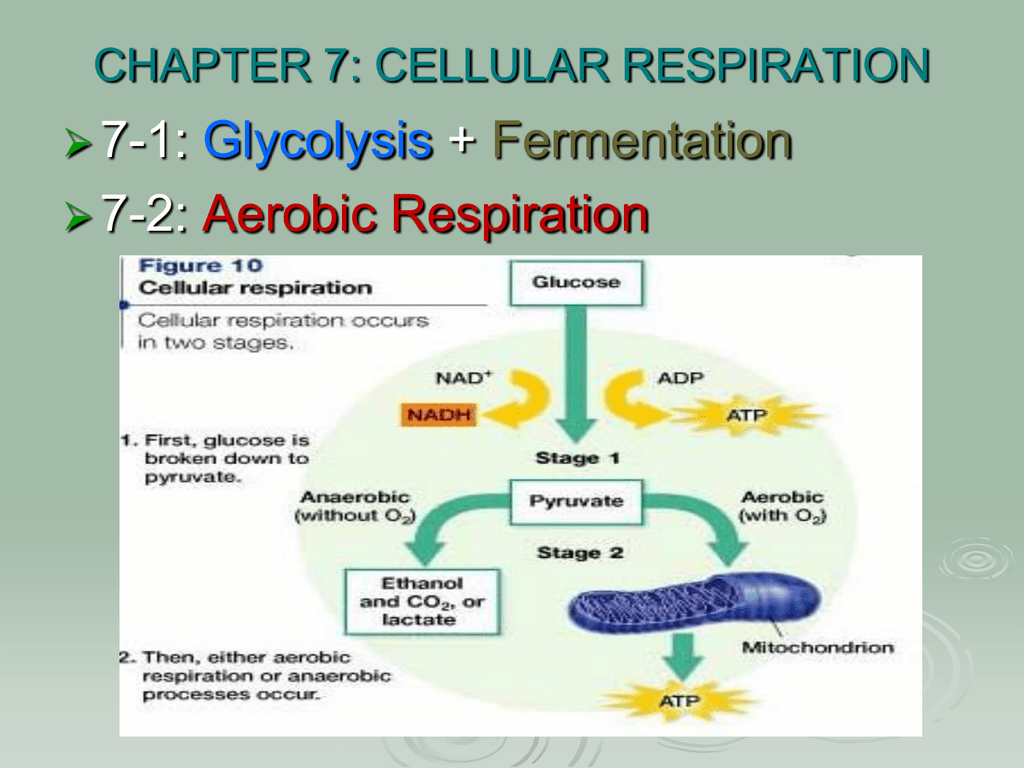
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration

Fermentation Anaerobic Glycolysis Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis And The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Mcat Content
Glycolysis And Fermentation Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Process Cycle Life Used Molecules Energy

Comments
Post a Comment